Do we have the freedom to choose?
It sounds like a simple question, but countless schools of thought claim that free will is an illusion.
On the one hand, determinists believe that every human action is determined by prior events, making free will nothing more than a trick created by our brains.
On the other hand is the libertarian outlook, which typically views people as fully responsible for their actions based on having free will.
There are many more moderate views that lie somewhere in between free will either being real or illusory. But before looking at free will from the human perspective, it might make more sense to see whether the trajectory of the entire universe is random, probabilistic or predetermined.
Many scientists have long thought that the inner workings of the entire universe – including human decision-making – is ultimately explainable at the quantum level.
The best place to look, then, might be quantum mechanics, the study of the universe at the smallest level. After that, we’ll see what all this has to do with humanity through the latest research in quantum consciousness.
A Thought Experiment – What’s in Control?
If the rate of technological advancement continues to keep pace, it’s conceivable that humanity will one day be able to create a digital universe based on the natural laws that govern our own. If this universe matches ours in terms of sophistication and complexity, life may arise.
Let’s imagine that evolution occurs in this digital world just as it did in our universe. In this hypothetical scenario, humans would exist within this digital replica.
These humans would not be controlled by us directly. Instead, they would think and behave just like us, making their own decisions and seemingly controlling their own outcomes within the framework of algorithms that dictate the natural laws of this universe.
These algorithms provide a framework for the digital universe, but they do not dictate the actions of the digital humans. The digital humans operate by the exact same natural laws as us, and therefore, exercise their own free will just like we do.
As creators of this digital universe, we possess the ability to manipulate time within it. Similar to how we can control a video or a game, we can fast forward, rewind, pause, speed up, and slow down the progression of events. This means we can observe any point in time within the digital universe.
So, are these humans in control of themselves? If not, what is?
Quantum Mechanics: A Very Brief and Simplified Guide
Without getting into the technicalities (we go into more depth with more analogies in the complete book, Monothology), here’s a quick look at what each of the key theories in quantum mechanics has to say about the trajectory of our entire universe – is it predetermined, probabilistic or random?
The Copenhagen Interpretation
In quantum mechanics, a quantum system, such as a particle, can exist in multiple (sometimes infinite) states simultaneously. The quantum system does not take on a single state until it is observed or measured.
You can think of it like rolling a die. While it’s rolling, it could be any number from one to six. Only when it stops will you be able to see which number it is.
A particle exists in all its states simultaneously – like a die that never stops rolling – until it is measured.
The Copenhagen Interpretation asserts that when we observe a particle, we only see one state of its superposition, which it then takes on indefinitely – all the other states of the superposition essentially disappear through a process known as the wave function collapse.
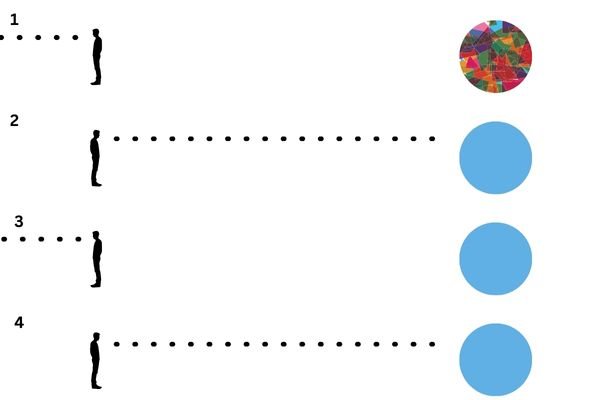
GTA Copenhagen
Imagine you’re playing a free-roaming game within a vast digital world, such as Grand Theft Auto. In this installation of the game, GTA Copenhagen, the entire map is always fully loaded, but each section of the map only takes on an appearance when you explore it for the first time.
Although the physical layout of the map is fixed, the game’s code has the potential to create the map with slightly different appearances before you start playing. When you enter a new area of the map for the first time, the roofs of the houses may be either grey, blue, brown or red. If the roofs take on a blue appearance the first time you see them, they’ll remain blue each time you revisit the area.
Copenhagen Interpretation and Free Will
What state a particle takes on comes down to probabilities. We can predict the outcome of an observation, but not with 100% accuracy.
So, with regards to free will – the Copenhagen Interpretation implies that the future is probabilistic, but not predetermined. In other words, we may have some control over our outcomes.
A problem with the Copenhagen Interpretation is the wave function collapse. While the theory explains why we can only observe a particle in one of multiple states, it doesn’t provide an explanation of what happens to the other potential states after the collapse or observation.
In the context of GTA Copenhagen – once you entered a new area of the map, the coding in the backend of the game’s framework produced a visual representation of black roofs. But the code that defined all other possible graphics does not disappear. Traditional quantum mechanics provides no explanation as to what the ‘unused’ code does or where it goes.
De Broglie-Bohm Theory
De Broglie-Bohm Theory suggests that all particles exist in all the states of their superposition all the time. We just see one state based on its trajectory through the spacetime continuum.
According to this theory, all particles have set trajectories – we could predict them with 100% accuracy with enough information. If this is accurate, then free will is nothing more than an illusion, and our entire universe represents what might be considered a pre-scripted design.
GTA Bohm
You’ve just got your hands on the latest installation of Grand Theft Auto, GTA Bohm. According to many critics, GTA Bohm has the best storyline of any installation yet. The story leaves no loose ends, and every subplot ties together with the overarching plot perfectly. However, with GTA Bohm, there is no gameplay. You just turn on the game and watch it play out.

Quantum Bayesianism (QBism)
QBism suggests that reality is fundamentally tied to and shaped by the preexisting knowledge, expectations and beliefs of observers. What form reality takes is a reflection of your observation, not an observation of reality in any preexisting state. I.e., your reality is shaped by your subjective experience.
GTA QBism
In GTA QBism, like in GTA Copenhagen, the map’s code allows for various visual possibilities. While all these potential appearances are encoded in the game, you will only see one, shaped by your pre-existing beliefs. For instance, if you believe roofs are generally black in the real world, you’re likely to see the roofs in the game as black as well.
But how does QBism explain how we all share the same reality?
Reconciling Our Subjective Realities
Basically, QBism proposes that although we all experience reality differently, we still observe the same fundamental rules of quantum mechanics. In the context of Grand Theft Auto, this means all players play within the same physical framework, even if their individual experiences of the game differ.
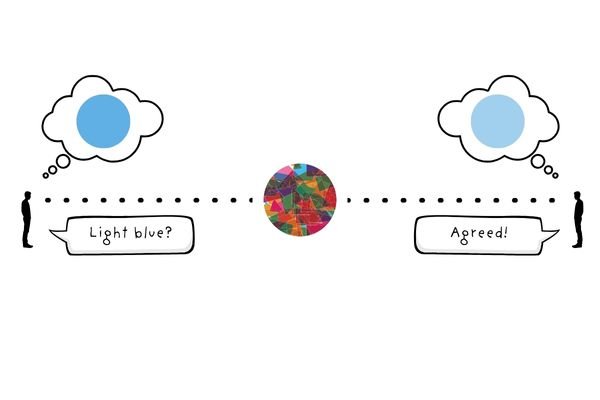
GTA QBism Multiplayer
You’ve decided to join a multiplayer game on GTA QBism, in which you and dozens of other players can roam around the same map. The map is fixed, allowing all players to occupy the same physical space and experience the same situations.
However, while all players occupy the same world, they’re all viewing it through different TV screens in separate rooms. Without knowing what the other players are seeing, each player assumes they are seeing the same thing.
Some TV screens display the sky as light blue, while other screens display the sky as a slightly lighter shade of blue. As the players describe the colour through their microphones, they all agree that the sky is light blue. Differences in perspective are consolidated.
Criticisms of QBism
QBism focuses on the subjective experience of the observer and doesn’t address what objective reality looks like when nobody is observing it. It also implies a significant degree of individual autonomy, with objective reality cocreated by the act of observation.
While QBism is appealing when it comes to free will, we might benefit from looking at what another theory in quantum mechanics has to say about our future.
The Many-Worlds Interpretation (MWI)
According to the MWI, when a particle is observed and takes on one state of its superposition, all the other states continue to exist in a parallel universe. Each time an observation (or measurement if caused by an interaction with something other than a human) is made, new parallel universes are created. And a particle can have infinite states in its superposition.
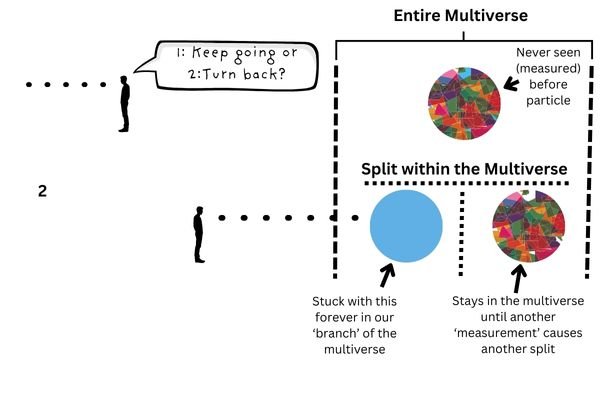
GTA Many-Worlds
On GTA Many-Worlds, you’re on a challenging mission to deliver a package within a time limit. Due to the challenging nature of this mission, there’s a checkpoint about halfway through.
The checkpoint is located just before an obstacle – a traffic jam. You must decide whether to turn around and try a different route, wait for the traffic to clear, steal a bike and slip between the vehicles, or walk through without raising attention.
Due to the game’s framework, the outcomes of all decisions are already scripted and are loaded as soon as you reach the checkpoint. But even though all the outcomes of all decisions are now in place, you’ll only experience one outcome based on your decision.
The MWI and Free Will
So, what does free will look like according to the MWI?
If this theory is accurate, every time you make a decision, all possible outcomes of that decision actually occur, but each different outcome takes place in a separate branch of the universe. For instance, if you decide to turn left in one branch of the universe, you’ll go right in a parallel universe. Both outcomes are realised, but in different branches.
Paradoxically, free will can’t truly exist according to the MWI given that every possible version of your life is playing out somewhere in the multiverse. But from your point of view in this branch of the universe, your future is not set in stone.
Do Quantum Events Have Anything to Do with Human Decision-Making?
Having a very basic and incomplete overview of quantum mechanics is all good and well, but does it even apply to human outcomes? Many scientists agree that all natural phenomena could be explained at the quantum level with enough information. Regardless of whether that’s true or not, groundbreaking research from this year suggests that our brains might actually be super-quantum computers.
Quantum Consciousness
Since the 90s, mathematician and physicist Sir Roger Penrose, along with anaesthesiologist Stuart Hameroff, have proposed that consciousness could arise from coherent quantum events in the brain.

Quantum coherence occurs when a collective of quantum systems, such as particles, synchronise their wave states. In coherent quantum systems, particles can maintain multiple states of their superposition, leading to constructive interference. This means that the coherent collective produces a higher wave amplitude than any individual particle can produce alone.
To put that into perspective – If ten violinists play the same song at the same time and volume in separate rooms, each produces up to 30 decibels of sound. However, if you put those ten violinists in the same room and they play in perfect synchronisation, their combined sound can reach up to 100 decibels.
Through the Orchestrated Objective Reduction (Orch-OR) Theory, Penrose and Hameroff demonstrate that consciousness might arise from ‘orchestrated’ quantum states in structural components of our brain’s neurons called microtubules.
For decades, Orch-OR was heavily criticised by a significant portion of the scientific community, with many sections preferring classical neurobiological explanations of consciousness.
In recent years, as more and more research has highlighted the potential validity of Penrose and Hameroff’s theories, Orch-OR has started gaining traction again. Evidence from recent experiments suggests that quantum processes may indeed take place in the brain as Orch-OR describes.
The Latest Groundbreaking Research
In 2023, using a highly sophisticated computational model, physicist and oncology professor Jack Tuszynski and the Orch-OR team shined light into a microtubule to see if it could retain quantum coherence similar to that in chlorophyll in plant cells.
If the energy transfer in microtubules could remain coherent for a fraction of a second, it’s likely that microtubules under biological conditions could indeed support quantum coherence. Across 22 experiments, the quantum reactions lasted up to thousands of times longer than expected.
In their 2024 paper, Ultraviolet Superradiance from Mega-Networks of Tryptophan in Biological Architectures, Babcock et al. demonstrate that the molecules and atoms in tryptophan (an amino acid in many proteins that make up living organisms) collectively emit light with greater intensity than any individual can emit alone. This amplification is possible due to quantum coherence.
While we can’t make any conclusive statements yet, the evidence in favour of our brains and potentially our entire bodies being super quantum computers is stacking up.
What Does All This Mean for Free Will?
If our actions and thought processes can be explained by quantum mechanics, then whether or not we have free will depends on which theory you find most convincing.
If you agree that the future isn’t predetermined and that we do have some sway over it, you might want to learn about the illusion of human autonomy to gain a more accurate perspective of your sense of control.
Then, you might want to learn more about the predictability of micro and macro quantum events, the neuroscience of volition, and their relation to the deterministic chaos theory by reading our full book, Monothology – which might just transform your entire world.
This article has been adapted from the book, Monothology: A Grassroots Science-Based Philosophy in ‘Self’ Transformation, which explores concepts ranging from neuroscience and evolutionary biology to the latest empirical research in quantum consciousness to dispel the human autonomy illusion and peel back the layers of the bigger picture of our existence. By understanding the illusions created by our minds, how we really operate as humans, and how to reflect objectively, Monothology helps you unlock self-awareness and boost emotional resilience.
Monothology presents a non-religious explanation of ‘God’ as the universe emerging, with our ‘Sense of God’ described through the lens of biology and evolution as an emergent cognitive function. It discusses how existing research suggests this Sense of God could be the origin of both religion and science.
We also explore the nature of free will, personal responsibility, mental health, increasing societal narcissism, and the meaning of life through groundbreaking and established research in neuroscience, evolution, quantum consciousness, particle physics, behavioural psychology, and much more.
Monothology: A Grassroots Science-Based Philosophy in ‘Self’ Transformation is available to purchase now at the Amazon Kindle Store for $9.99.










0 Comments